The First Electric Vehicle Car and Driver Ever Reviewed, from 1960
From the January 1960 issue of Sports Cars Illustrated.
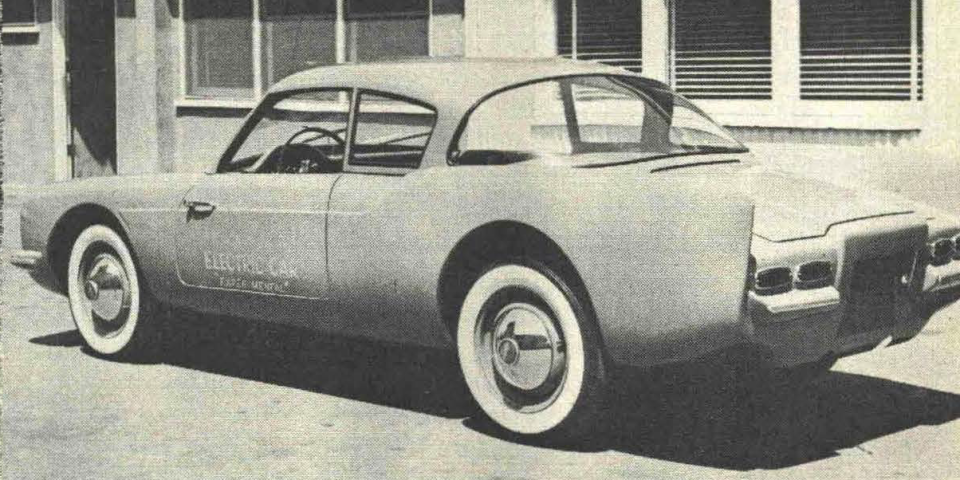
We recently drove a car that, when it reaches production, could take the second-car market by storm. The most unusual automobile of conventional configuration to be engineered in this country in many years, it will be manufactured by the Nic-L-Silver Battery Company of Santa Ana, California. There will be no gasoline or air pollution problems with the "Pioneer," as it is called, for this is the most promising to date of the several electric cars being engineered in various cities. Tests thus far indicate operating costs will be under ⅓ cent per mile.
The two-seater body is of laminated fiberglass by Alken with a removable hard top that attaches by four thumb screws. Behind the individual bucket seats, which move far enough back to allow a six-footer reasonable comfort, are 12 4-volt series-wired batteries of special design made by Nic-L-Silver. Concealed beneath rugged flooring which serves as luggage space, these lead-acid batteries have two cells each with 31 plates per cell and a capacity of eight hours at 235 ampere-hours.
A box section steel frame of simple but rugged construction carries the full torsion-bar suspension, which closely resembles the Volkswagen layout. Two electric motors, each delivering eight shaft horsepower, are used; there is one to each rear wheel, the latter being driven by a rugged sprocket and chain system that is geared down to conserve power. Top speed is 50 miles an hour, but acceleration to this maximum is amazingly brisk, quicker than that of the average small imported car.

Driving is simple and most enjoyable. The seats are as comfortable as those in most small sports cars. In fact one sits very low with the legs outstretched. There are two pedals, one being the usual brake pedal which operates a conventional hydraulic system with expanding shoe brakes with one slave cylinder in each wheel. The other pedal is a wide one for acceleration with an operation best described as two-stage. For normal driving at city traffic speeds, 25 to 35 miles an hour, the accelerator is depressed less than halfway, and the drain on the batteries is 24 volts at the most. For full acceleration and speeds approaching the maximum, the pedal is depressed past the halfway mark, whereupon the voltage used approaches or attains the maximum of 48 volts.
The steering system is also conventional recirculating-ball type, with very easy movement of the wheel even at rest requiring three turns from lock to lock. As the wheelbase is just 95 inches, the Pioneer will turn on a dime; parking will be a breeze with space to spare due to the overall length of 157 inches. The overall width is about 60 inches which should qualify this little runabout for reduced parking rates in many public parking lots.
George Lippincott, the founder and president of Nic-L-Silver, hopes to have 10 cars a day rolling off the assembly line now being tooled. Power companies, postal authorities, and dealers throughout the West Coast states are interested in obtaining the first models. As quickly as possible, according to Lippincott, the Pioneer will be produced at a rate of one hundred a day, national distribution being the eventual intention. The Pioneer has been tested in San Francisco where it devoured the city's famed steep hills in front of utility officials and interested dealers.
The weight of the Pioneer, with the hardtop in place, is 1800 pounds of which over 600 are accounted for by the batteries. The fiberglass body weighs less than 300 pounds.

 Yahoo Autos
Yahoo Autos 