How To Bulletproof a Car
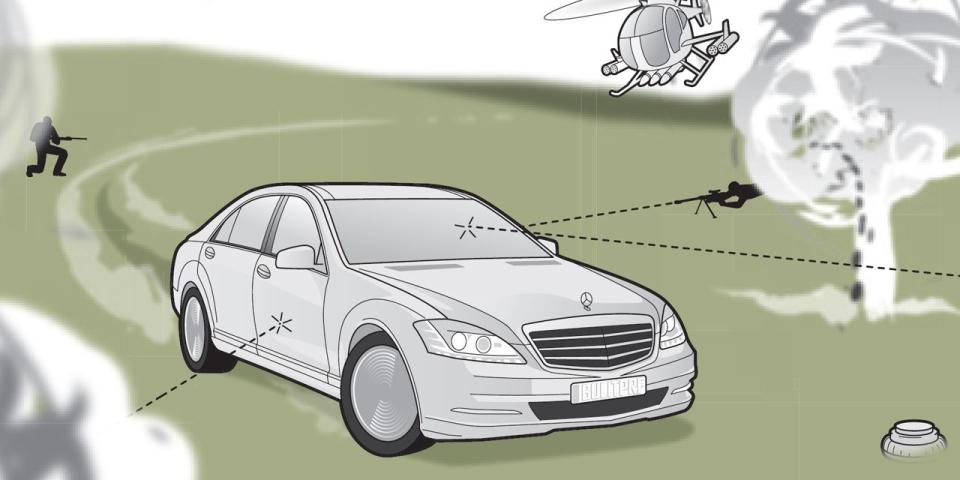
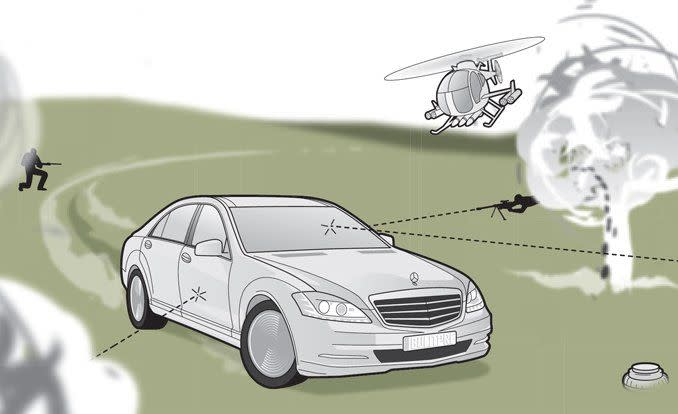
Armoring passenger cars has become big business, especially in places such as Brazil, where the murder rate is five times that of the big, bad U.S. of A. Although automakers have tiptoed into the bulletproofing game—BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and for a time, Ford, have offered bulletproof versions of their products—the vast majority of cars are modified by aftermarket companies like International Armoring Corporation (IAC) of Ogden, Utah, which has armored more than 5500 vehicles since 1993. The company will make bullets bounce off a new BMW 750i for a minimum of $52,500, though that tab can rise above $100,000 should the owner opt for defenses such as smokescreens and electric shocking. By the way, we’re only kidding about bullets “bouncing off” armored cars—the armor actually works to absorb gunfire. Here’s how it’s done.
DOORS, BODY, AND INTERIOR
The first step is to remove all of the components from the car’s body (interior trim, wiring, carpet, seats, etc.). Then the doors and all other cavities (such as the pillars) are cut open so various materials can be stuffed or welded into those voids. Depending on the level of protection desired, the doors and pillars might be bolstered with steel plates, a combination of ballistic nylon and Kevlar (similar to the material in bulletproof vests), or both. If the doors get too heavy, a third hinge is added. The fire wall and rear bulkhead can be steel-plated, too, but the floor and ceiling are generally lined with ballistic fabrics. The stock bumpers, designed to crumple and absorb energy during major impacts, can be reinforced to allow the armored car to, for example, bash through an improvised roadblock without damaging the radiator. The goal of armoring is also to make the car appear to be unmodified, inside and out.
GLASS
In the bulletproofing biz, glass is referred to as “transparent armor.” It is not a thicker version of the safety glass found in the side windows of standard cars but rather a sandwich of polycarbonate (a type of plastic) and leaded glass. The thinnest option—0.8 inch—will stop subsonic rounds such as those from the popular 9mm handgun, while the thickest glass—2.0 inches—should emasculate a single shot from a high-powered .30-06 rifle. If necessary, the electric window motors can be replaced by beefier ones.
TIRES
Conventional run-flat tires can’t stand up to gunfire because bullets could shred the stiff sidewalls these tires rely on for support. IAC uses a Hutchinson-made Composite RunFlat tire, which is a polymer donut custom-built for each application. It is clamped around the centerline of a wheel, inside the tubeless tire, and the working principle is similar to the Michelin PAX System’s: If the pneumatic tire loses pressure, the polymer ring provides support that allows 60-mph speeds for more than 60 miles.
SUSPENSION AND ENGINE
Even the lightest armoring adds at least 500 pounds to a large sedan. With the greatest level of protection for a large sedan adding 1400 pounds, it is necessary to modify the chassis and occasionally the drivetrain. To maintain drivability, damping and spring rates rise, and air springs slot in if needed. Most modern engines in large sedans have enough power to sufficiently cope with the extra weight, so engine modifications happen only if specifically requested by the customer. Three-quarter-ton trucks and SUVs are the only vehicles with underpinnings capable of bearing the roughly 2000 pounds of the highest level of protection without any modifications.
From the December 2009 print issue of Car and Driver
You Might Also Like

 Yahoo Autos
Yahoo Autos 