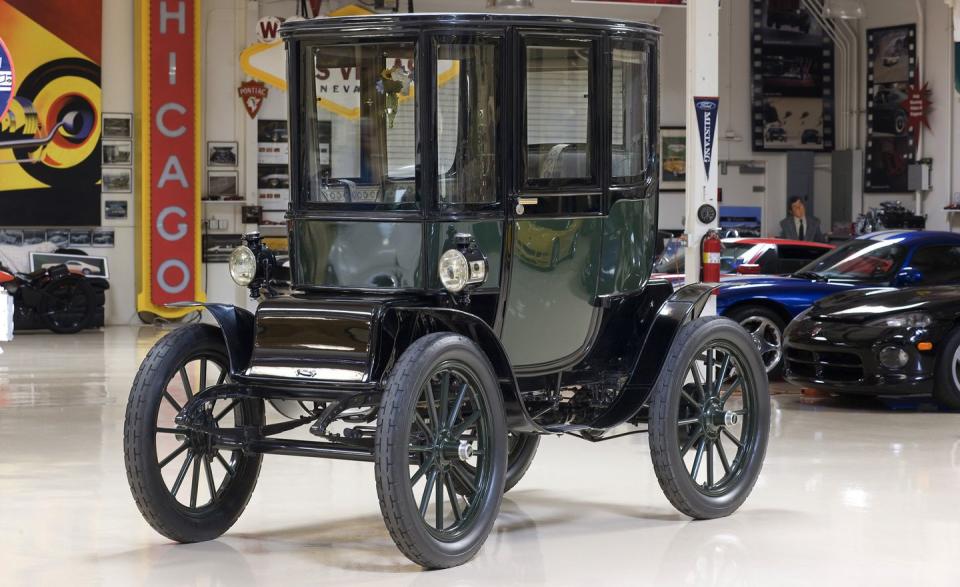
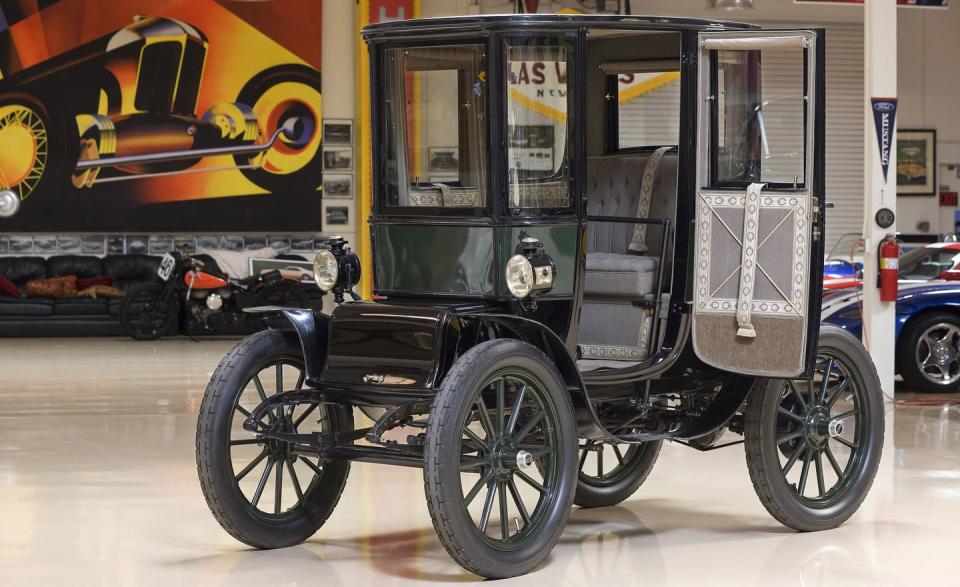
An Electric Pioneer: Cleveland’s Baker Electric

In the first decades of the 20th century, electric vehicles seemed poised for primacy. Early internal-combustion engines were rudimentary, dangerous, and difficult to operate, requiring all sorts of pump priming and starter torqueing. Those tasks were uncouth for the wealthy gentlemen who were the automobile’s first customers and downright risky for the era’s women, clothed in voluminous, billowing Edwardian dresses and patriarchal notions of competence. Electric cars, on the other hand, were extremely simple to use. So long as the heavy batteries were maintained and charged, all one had to do was click the on switch, twist the go lever, and roll.
Having founded the American Ball Bearing Company in 1895, Midwestern engineer Walter C. Baker understood the basics of carriage production. This background gave him faith that he could make the leap into car building. Teaming up with his father-in-law and brother-in-law, he started the Baker Motor Vehicle Company in Cleveland in 1899. Seeing the aforementioned advantages inherent in electric vehicles, Baker decided to place his faith in this powertrain.
“Number one, it’s comfortable, and it’s not terribly difficult to drive,” said Stew Somerville, a volunteer mechanic at the Old Rhinebeck Aerodrome museum in upstate New York, which holds a 1911 Baker in its eclectic collection. “But part of the attraction of the electric automobile was the fact that it did not emit gasoline fumes, you didn’t have to crank-start the engine, there was no big wheel to wrestle with. It was a very smooth-handling automobile. You didn’t even have a loud, offensive horn. There’s a dainty little bell to warn of its coming.” Period ads were frequently, although not exclusively, pitched directly at women.
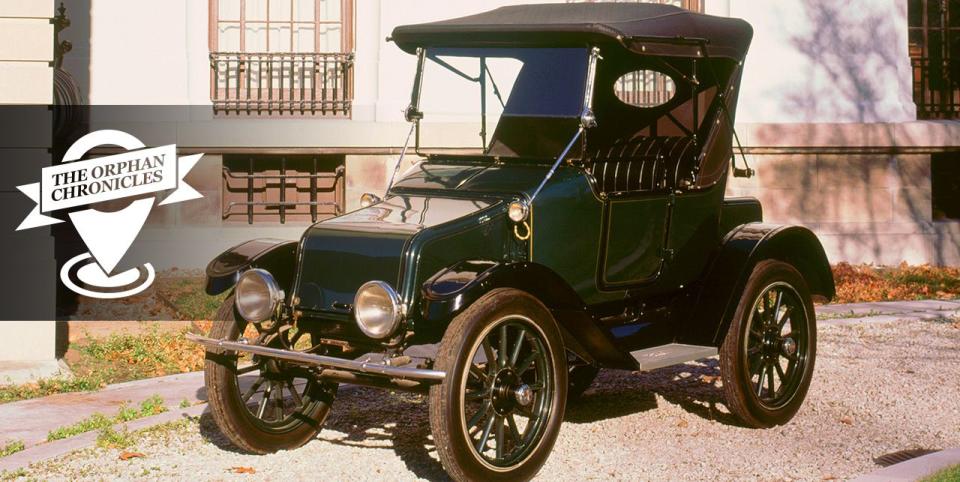
Baker’s first car to market was a two-seater, the Imperial Runabout. Priced at a competitive $850, it was first shown in New York at the city’s (and nation’s) first auto show. It attracted a number of notable buyers, including Thomas Edison, who purchased one as his very first car. (Edison designed the long-lived nickel-iron batteries used in some Baker vehicles.) By 1906, Baker was, briefly, the world’s top producer of electric vehicles.
But like many of his cohort in the emergent automotive industry, Baker wasn’t just in it for the business. He was in it for the speed. As his company was enjoying success in the consumer market, he was pursuing his dream by developing a series of advanced, record-setting racing cars. His first, the Torpedo, was built in 1902, at great personal expense to Baker. With its 11 batteries, 14-hp mid-mounted motor, outrageously low-slung 48-inch height, streamlined and lightweight white-pine and oilcloth body, and bizarre webbed canvas seat restraints, it seemed poised to set a world land speed record.
Sadly, in at that year’s Automobile Clubof America speed trials on Staten Island, the car was involved in a disastrous crash. After crossing the 1-kilometer (0.6 mile) mark in just over 30 seconds, Baker and his co-driver lost control and crashed into a group of spectators. One person died at the scene, and another died later from injuries. The drivers were both arrested and charged with manslaughter but were freed when it was determined that the crowd had pushed past protective barriers and onto the course. (Baker’s innovative safety harness likely protected the car’s occupants from serious injury.)
Further attempts with two smaller, single-seater race cars he named Torpedo Kid were also employed in pursuit of the land speed record but were subsequently abandoned following another, nonlethal spectator crash in 1903. Baker has often been noted as the first person to cross the 100-mph barrier, although his records weren’t official due to these wrecks.
Given this peril, Baker decided to forgo his quest for top speed. As gasoline-powered vehicles increased in popularity and gained infrastructural support, he shifted his attention instead to diminishing the electric car’s liabilities, particularly their limited range. He worked diligently on new battery designs, shaft drives, and other componentry. In 1910, Baker’s new chief engineer, Emil Gruenfeldt, set a record for distance driven on a single charge, taking a Baker Victoria for a 201-mile trip at an average speed of 12 mph. Not exactly Ludicrous speed, but an impressive feat nonetheless.
Baker’s successes gave the company prominence among the elite, and the company capitalized on this publicly. In advertisements around 1909, the brand boldly boasted about the King of Siam owning a Baker. The company made a similar splash in American politics when President William H. Taft’s administration purchased a 1909 model as one of the White House’s first automobiles. (A steam-powered White and two gasoline-powered Pierce-Arrows were also included, Taft hedging his bets on how the battle of the powertrains was going to play out.) Taft later added a 1912 Baker Victoria that went on to be driven by five First Ladies. The Baker brand maintains some celebrity allure today, with car-collecting comedian Jay Leno holding a 1909 model in his expansive collection.
As a means of offsetting some of the powertrain’s inherent shortcomings, Baker made investments in battery-charging infrastructure. The brand announced plans to open stations at every major intersection in Cleveland and to grow the network from there, although this effort became cost prohibitive and never came to fruition. Expansion into the production of electric trucks, police patrol wagons, and even trucks and bomb handlers for the U.S. Army during World War I was not enough to fend off the rising dominance of the internal-combustion engine, especially after the proliferation of the electric starter, first available on the 1912 Cadillac, significantly increased safety and convenience. By 1915, the Baker company was defunct.
Previous Orphan Chronicles: Anderson | Edwards | ReVere
“We don’t understand why it has taken so long for the electric automobile to regain its popularity in the United States,” says the Rhinebeck Aerodrome museum’s Somerville. “Driving today is very tactile and very audible. But driving a Baker electric is unlike anything you’ve ever seen or heard. It’s silent, and you’re alone with your thoughts-and you don’t have to do a heck of a lot of thinking.”
You Might Also Like

 Yahoo Autos
Yahoo Autos