Why the Ferrari F355 Sounds So Good
The sound is unmistakable—rich, complex, cultured, yet ferocious. Even among Ferraris, the noise emanating from the F355 is unique. After a recent opportunity to drive a manual F355 Berlinetta, fulfilling a childhood fantasy, the noise burnished itself in my brain. I walked away with two wants, a manual F355 Berlinetta—ideally in blue—and to drill down into its specific sound.
Seeing as I can't afford a 355, I'll write about the sound for now. We should start with the fundamentals. Literally. While in carbureted sports cars intake noise might mean everything, and for certain luxury cars ultra-quiet valvetrain noise might be paramount, for cars like the F355, the dominant sound is the exhaust. The exhaust sound is specifically the pulses of air that run from exhaust valve to tailpipe. The dominant frequency made by these pulses can be determined with simple math. Divide engine speed by 60, and you get a value in hertz, or cycles per second. As a four-stroke engine only fires twice for every rotation of the crankshaft, multiply that number by half the cylinder count. So for an eight-cylinder engine running at 3000 RPM, 3000/60 is 50 hZ; multiply 50 by 4 and you get 200 hZ. (For musicians, that's around the G#/Ab just below middle C, and how I verified my math.)
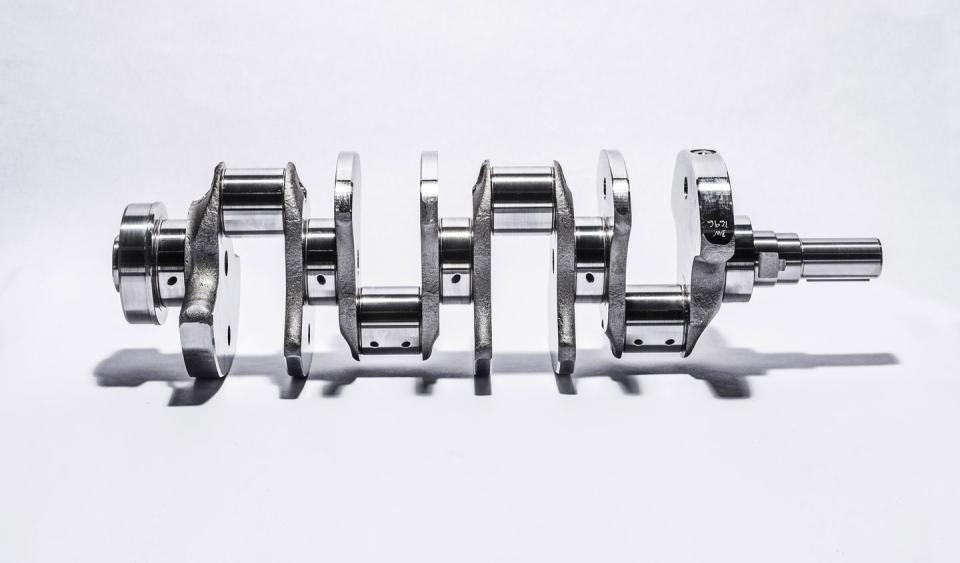

Chances are you've heard of the two types of crankshafts used by V-8s, flat-plane and cross-plane. The vast majority of V-8s use a cross-plane crankshaft, which has pairs of crankpins offset by ninety degrees. This gives an uneven firing order between cylinder banks of left-right-left-left-right-left-right-right, which presents audibly as the distinctive V-8 burble you know and love. A cross-plane crank is best for minimizing vibrations, though this comes at the expense of weight, and thus maximum possible engine speed.
A flat-plane V-8 uses a crankshaft with crankpins offset by 180 degrees. Unlike a cross-plane V-8, a flat-plane V-8 fires evenly between cylinder banks, which incidentally, means it behaves a lot more like two four-cylinders with a common block and crank. This also gives it quite a different sound, a lot more four-cylinder-esque, as the exhaust pulses from each side of the engine arrive at our ears at evenly spaced intervals. Flat-plane V-8s aren't as smooth as cross-plane V-8s, but their crankshafts are much lighter, allowing for higher revs. Ideal for, say, a Ferrari sports car, but not a Chevy pickup. While these two types of V-8 sound very different, the math to calculate the primary pitch for a given RPM is still the same. With flat-plane vs cross-plane V-8s, we're talking about a difference in tone here, not pitch, though given a flat-plane crank allows for high revs, the engine is therefore capable of producing a higher-pitched sound.
Still, the timbre or tone of a flat-plane V-8 is distinctive to its cross-plane brethren, and that's why the F355's V-8 sounds different from, say, a 1995 Corvette's small-block. But while a lot of Ferrari V-8s–all of which are flat-plane—are tonally similar, the F355's, and by extension, the 360 Modena's mechanically similar 3.6-liter, are still unique. And unique among all flat-plane V-8s, except one from Detroit.
That Detroit V-8 is, as you may have guessed, the new Corvette Z06's LT6 V-8, a 5.5-liter flat-plane unit designed specifically for this model. Early last year, Chevrolet held a virtual briefing for the media where they pored over the details for the LT6, and it's proven instrumental—no pun intended, at least not consciously—for my understanding of the Ferrari F355's V-8. The engineers tried to emphasize two frequencies above all, the fourth and eighth order.
The fourth order is another name for the dominant frequency produced by a running V-8, so called because the frequency is four times the frequency of crankshaft rotation. (The sound a four-cylinder makes is a second order, a six-cylinder a third order, and so on and so forth.) What I find particularly interesting is that eighth order. You can calculate the eighth order frequency by using the same formula to determine dominant frequency, but just multiply your engine speed in hZ by eight. In the case of an engine of any cylinder count spinning at 3000 rpm, you get an eighth order frequency of 400 hz. With both our Z06 and F355 V-8 at 3000 rpm, the 200 hz fourth order and 400 hz eighth order blend to provide an octave, the same note at two different frequencies. (Think "do-re-mi–fa-sol-la-ti-do," if we want to relate this back to Western 12-tone equal temperament.)

 Yahoo Autos
Yahoo Autos 